AI·빅데이터 융합 경영학 Study Note
[ML수업] 10주차 실습4: pipeline_stacking 예시 코드1 본문
# Authors: Guillaume Lemaitre <g.lemaitre58@gmail.com>
# Maria Telenczuk <https://github.com/maikia>
# License: BSD 3 clause
1. Download the dataset
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
def load_ames_housing():
df = fetch_openml(name="house_prices", as_frame=True, parser="pandas")
X = df.data
y = df.target
features = [
"YrSold",
"HeatingQC",
"Street",
"YearRemodAdd",
"Heating",
"MasVnrType",
"BsmtUnfSF",
"Foundation",
"MasVnrArea",
"MSSubClass",
"ExterQual",
"Condition2",
"GarageCars",
"GarageType",
"OverallQual",
"TotalBsmtSF",
"BsmtFinSF1",
"HouseStyle",
"MiscFeature",
"MoSold",
]
X = X.loc[:, features]
X, y = shuffle(X, y, random_state=0)
X = X.iloc[:600]
y = y.iloc[:600]
return X, np.log(y)
X, y = load_ames_housing()
2. Make pipeline to preprocess the data
scikit-learn의 make_column_selector 기능을 사용하여 특정 데이터 유형을 기준으로 열을 선택하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이를 통해 데이터 전처리에서 범주형 또는 수치형 데이터를 쉽게 구분하고 처리할 수 있습니다.
from sklearn.compose import make_column_selector
cat_selector = make_column_selector(dtype_include=object)
num_selector = make_column_selector(dtype_include=np.number)
#num_selector(X)
#cat_selector(X)
3. design the pipeline required for the tree-based models. Then, define the preprocessor used when the ending regressor
is a linear model.
from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder
cat_tree_processor = OrdinalEncoder(
handle_unknown="use_encoded_value",
unknown_value=-1,
encoded_missing_value=-2,
)
num_tree_processor = SimpleImputer(strategy="mean", add_indicator=True)
tree_preprocessor = make_column_transformer(
(num_tree_processor, num_selector), (cat_tree_processor, cat_selector)
)
tree_preprocessor
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler
cat_linear_processor = OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore")
num_linear_processor = make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(), SimpleImputer(strategy="mean", add_indicator=True)
)
linear_preprocessor = make_column_transformer(
(num_linear_processor, num_selector), (cat_linear_processor, cat_selector)
)
linear_preprocessor
4. Stack of predictors on a single data set
from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV
lasso_pipeline = make_pipeline(linear_preprocessor, LassoCV())
lasso_pipeline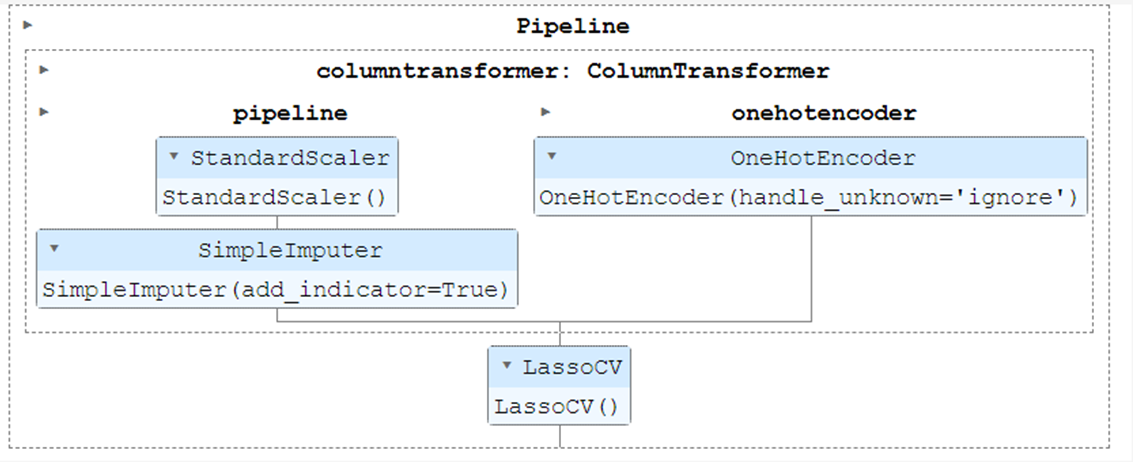
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
rf_pipeline = make_pipeline(tree_preprocessor, RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42))
rf_pipeline
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingRegressor
gbdt_pipeline = make_pipeline(
tree_preprocessor, HistGradientBoostingRegressor(random_state=0)
)
gbdt_pipeline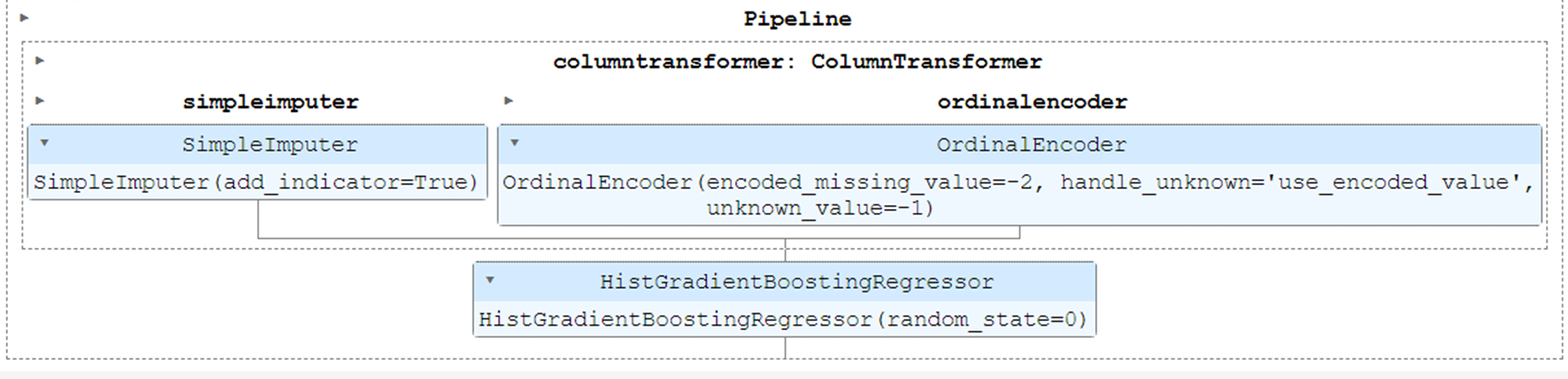
from sklearn.ensemble import StackingRegressor
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV
estimators = [
("Random Forest", rf_pipeline),
("Lasso", lasso_pipeline),
("Gradient Boosting", gbdt_pipeline),
]
stacking_regressor = StackingRegressor(estimators=estimators, final_estimator=RidgeCV())
stacking_regressor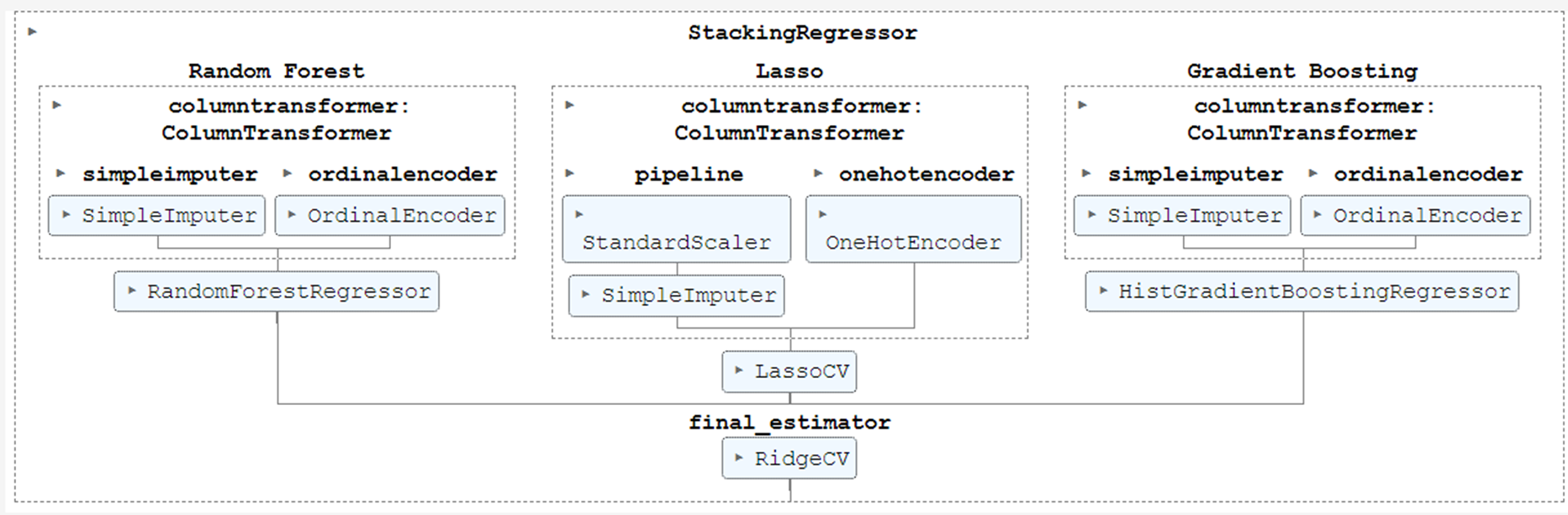
5. Measure and plot the results
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
for m in estimators + [("Stacking Regressor", stacking_regressor)]:
scores = cross_val_score(m[1], X, y, scoring="neg_mean_absolute_error")
print(f"{m[0]}: {scores.mean()*-1:.3f}")'AI·ML' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ML수업] 8주차 실습1: feature engineering- Missing Data Handling (0) | 2023.11.30 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬 다 돌아가면 소리남 (0) | 2023.11.23 |
| [ML수업] 10주차 실습2: Hyperparameter Tuning using Pipeline+Optuna 예시 코드 (0) | 2023.11.21 |
| [ML수업] 10주차 실습1: pipeline_basics (0) | 2023.11.21 |
| [ML수업] 8주차 실습6: feature engineering- Feature Generation (0) | 2023.11.21 |


